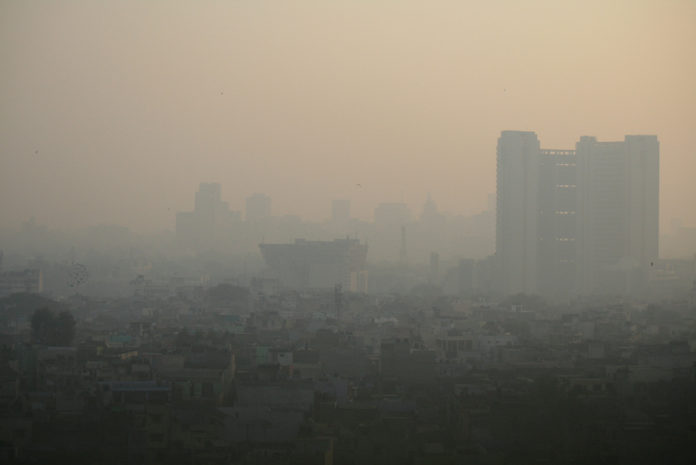
New Delhi, the capital of India, has arguably become the pollution capital of the world. The latest Air Quality Index (PM2.5), according to the latest figures is 390. This comes in the severely polluted category. Any level below hundred is counted as polluted.
Winter conditions with winds coming from neighbouring states of Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh add to the pollution. This wind contains many toxic dust particles.

Researchers Mohit Saxena, A Sharma, Saraswati, T K Mandal, S K Sharma, C Sharma from the National Physical Laboratory and Priyanka Saxena from the National Environmental Engineering Research Institute conducted a study on the pollution levels of the city.
Their study found that the winter smog and pollution in Delhi was a result of winds coming in both from north west and east– 72 percent from Pakistan and northern states of India and 28 percent from its east

Further, the study found ,” Particulate matter 2.5 mass concentration in summers was 52 percent because of winds travelling across southern Afghanistan, northwestern Pakistan and 35 percent from the eastern part of India. In winter and spring seasons, the sampling site was affected by cold air masses arriving from the northern parts of India and Pakistan 46 percent and 30 percent from the adjoining states of Delhi.” During monsoons, 53 percent of wind comes from east of Delhi, 25 percent from northern and northwestern parts like Afghanistan, Pakistan and 22 percent from the Arabian Sea.
Purpose of study:
To understand the variety of pollutants that reach Delhi from different parts of the country, depending on the seasons, the National Physical Laboratory conducted another study. The following results show the contribution of different causes for the particulate matter:
14 percent- biomass burning
21.3 percent- secondary aerosols
20.5 percent- soil dust
19.7 percent- vehicle emissions
13.7 percent-fossil fuel combustion
6.2 percent-industrial emissions
4.3 percent- sea salt